DataSpec: Open Source Data Infrastructure
For smaller data teams, paid tools like Tableau, Power BI, Snowflake, and SQL Server can be unnecessary and expensive, if your requirements do not need that level of scale.
If you want more control over your data infrastructure, using open source tools is a viable alternative.
However, one of the barriers to adopting open source software is the effort required to integrate them together.
DataSpec aims to speed up that deployment process by wrapping major data infrastructure components in docker containers with per-configured defaults, so that you can focus more on building, not wiring services together.
Below are the services in each container:
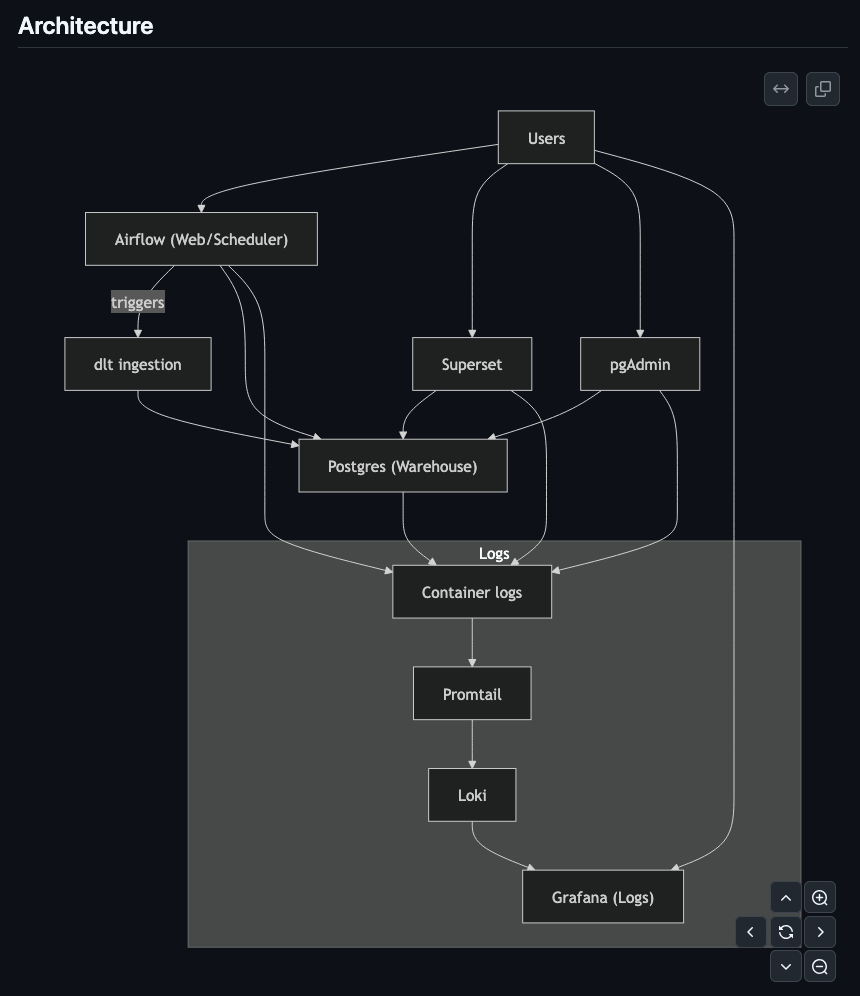
Data Ingestion
Airflow: orchestration for jobs
DLT: library that loads data into a database
PostgreSQL: open-source database
pgAdmin: Web UI for PostgreSQL
Superset: Open-source Business Intelligence tool
promtail: reads logs from docker containers
loki: stores logs
grafana: shows logs via loki
I will go over each of these components.
Architecture Diagram
Docker
Docker packages an application and all of its dependencies into a container so it can run consistently across environments. It builds images from Dockerfiles, which define the runtime environment, then runs containers as isolated processes on a host. Instead of virtualizing hardware like a traditional VM, Docker uses operating system level isolation through namespaces and control groups, sharing the host kernel. On Linux, it runs natively; on macOS and Windows, it runs inside a lightweight Linux virtual machine managed by Docker Desktop. Because the image fully defines the environment and the runtime is consistent, containers can be built once and run the same way across operating systems.
Airflow
Airflow is a workflow orchestration platform that schedules and manages data pipelines defined as directed acyclic graphs. Each DAG describes tasks and their dependencies in Python. The scheduler continuously parses DAG files, determines which tasks are ready to run, and creates task instances. Runnable tasks are sent to an executor, which dispatches them to workers for execution. Workers run the actual code and update state in the metadata database. The webserver reads from this database to display pipeline status and history in the UI.
dlt
dlt is a Python based data loading framework that standardizes how data is extracted, transformed into structured tables, and loaded into analytical databases. You define data sources and resources in Python, and dlt handles extraction details such as pagination and batching. It normalizes nested data into relational tables, automatically infers and evolves schemas, and tracks incremental state to support resumable and change data capture patterns. Finally, it loads the processed data into the target destination using idempotent writes, ensuring reliable ingestion.
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is an open source relational database that stores structured data in tables and allows querying with SQL. It supports standard SQL features, indexing, and complex queries while ensuring ACID compliant transactions for consistency. Using multiversion concurrency control, it allows many users to read and write data simultaneously without blocking each other. It is extensible, supporting advanced data types like JSON and custom functions, making it suitable for both transactional systems and analytical workloads.
pgAdmin
pgAdmin is a graphical interface for managing PostgreSQL databases. It connects to PostgreSQL servers and allows users to browse databases, schemas, tables, and views through a visual interface. It includes a built in SQL editor for writing and running queries, along with tools to manage users, roles, and permissions. It also Provides utilities for viewing query plans and monitoring server activity, making administration more accessible without relying solely on the command line.
Superset
Apache Superset is a web based business intelligence platform used to explore and visualize data stored in databases. It connects to systems such as PostgreSQL or Snowflake and allows users to write SQL queries or build datasets. Query results are rendered as charts and dashboards with interactive filters and drill downs. Superset also manages user authentication and permissions, acting as a visualization layer on top of existing databases.
Promtail
Promtail is a lightweight log collection agent that gathers logs and sends them to Grafana Loki. It monitors configured log files or system sources, reads new lines as they are written, and attaches labels such as application or host metadata. It tracks file positions to avoid reprocessing logs and pushes labeled log streams to Loki over HTTP. Its primary role is log shipping rather than storage or analysis.
Loki
Grafana Loki is a log aggregation system designed to efficiently store and query logs. It receives labeled log streams from agents like Promtail and stores the raw logs in compressed chunks. Instead of indexing the full text of logs, it indexes only the labels, which reduces storage overhead and improves scalability. Users query logs using LogQL, filtering by labels and searching within log content. Loki integrates closely with Grafana for visualization and exploration.
Grafana
Grafana is a visualization and monitoring platform that displays metrics, logs, and other time series data from various data sources. It connects to systems like Prometheus, Loki, or SQL databases and allows users to define queries within dashboard panels. When a dashboard loads, Grafana sends queries to the underlying data source, receives the results, and renders charts and visualizations in the browser. It also supports alerting, user authentication, and access control, serving as a central observability interface.
Getting started
Install Docker.
Issue the following command: git clone https://github.com/jordansgoodman/dataspec dataspec
Switch to the dataspec directory.
Run: docker compose up.
All of the services will start up, binding to various localhost ports.
For more information, visit github.com/jordansgoodman/dataspec.